GEO: Generative Engine Optimization Explained
Everything you need to know about GEO: how search is changing and what you should do about it.
Akash Bhadange
May 30, 2025 • 5 min read
Search is no longer just about links. It’s about answers.
Over the past two decades, we’ve optimized our content to perform well in traditional search engines like Google. We studied SEO tactics, optimized our metadata, chased backlinks, and learned how to climb the rankings.
But the way people discover information is rapidly evolving.
When someone asks ChatGPT or Perplexity a question and gets a response that doesn’t require clicking a single link, they’re not browsing search results. They’re asking questions and interacting with a generative search engine.
This fundamental shift is why Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) is the new battleground for content visibility.
What is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)?
GEO is the practice of structuring your content so that it can be understood, referenced, and cited by AI-powered generative search engines like ChatGPT, Claude, Perplexity, Bing Copilot, and Google’s SGE (Search Generative Experience).
These engines don’t present a list of ten blue links. Instead, they synthesize information across the web and serve it as a direct answer. Your content can be included in these answers in different ways. Sometimes the AI will quote your content exactly as you wrote it. Sometimes it will reword your ideas in a simpler way. It may also include a link to your site, or it might just use your content in the background to help shape its answer, even if you don’t get direct credit.
The important thing is that your content is not being ranked in a list. It is being picked up and used inside the answer itself. That is what makes GEO different. It is not about getting to the top of a search page. It is about being part of the answer.
Why GEO is Fundamentally Different from SEO
From Queries to Conversations
SEO optimizes for specific keyword searches: “best CRM for small teams” or “how to train a golden retriever.” GEO, on the other hand, prepares your content to serve natural language questions in conversational contexts like:
“I’m starting a company: what’s the easiest CRM to set up?”
“How can I train a 3-month-old golden retriever not to bite?”
These AI models don’t just match keywords. They interpret intent. And that means your content must match underlying meaning, not just phrasing.
From Clicks to Citations
In SEO, success is measured by click-through rate (CTR). You want users to see your link and visit your site.
In GEO, success is measured by inclusion or citation in the AI’s response, even if the user never clicks.
You’re optimizing to be part of the answer, not just a link beneath it.
From Optimization for Search Engines to Optimization for Language Models
Search engines operate through indexing and ranking algorithms. Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-4 or Claude operate through semantic understanding. They:
Read your content holistically
Identify key concepts and relationships
Generate responses based on context and probability
That means structure, clarity, and precision matter more than ever. LLMs are not looking for keyword density, they’re looking for trustworthy, clear, and concise information that’s easy to repurpose.
Why GEO Matters More Than Ever
AI tools like Perplexity and ChatGPT are no longer just assistants. They are becoming the starting point for how people discover information. These engines don’t merely summarize content. They decide what matters. If your content isn’t being surfaced in their responses, it might as well not exist.
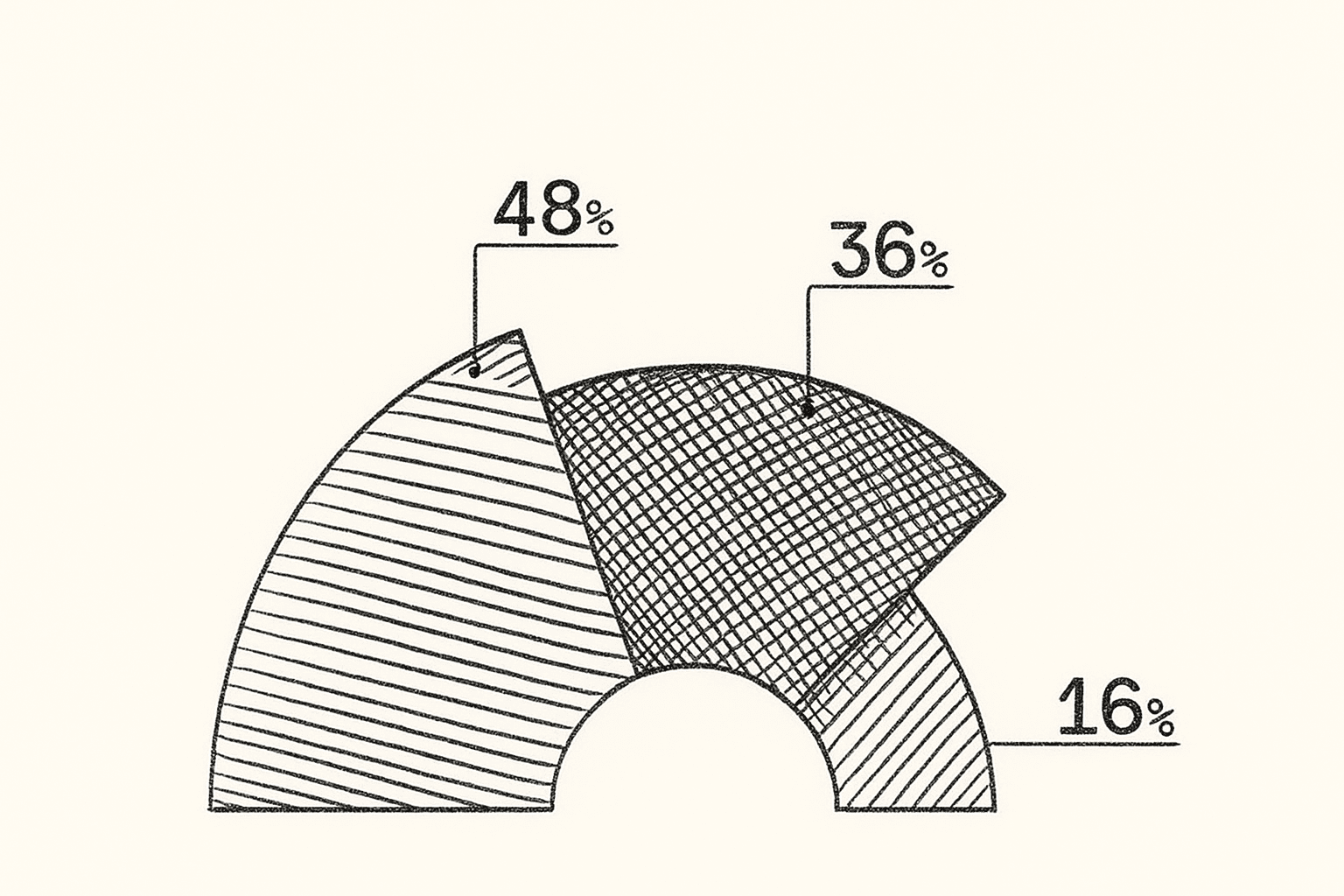
The shift is already visible. Major publishers are watching their referral traffic from Google decline. Queries that once drove thousands of visits are now absorbed by AI-generated answers. This is not a blip. It is a structural change in how the internet works.
And yet, GEO is still early. While SEO has matured into a highly competitive space, Generative Engine Optimization is just beginning. Most content creators have not caught on. That gives early adopters a rare advantage. A chance to own a niche before it becomes saturated.
This is not just about traffic. It is about authority. When ChatGPT or Google’s AI Overview quotes your content, it is signaling to the user that your voice is credible. Inclusion in AI answers is quickly becoming a new form of trust.
This “machine trust” is increasingly shaping human trust.
How Generative Engines "Find" and "Use" Your Content
Most generative engines today work in three ways:
Pretrained Knowledge: Some engines (like ChatGPT with its cut-off knowledge) are trained on vast internet corpora. If your content was included in its training set, it might be used—though not cited.
Real-time Retrieval (RAG): Modern AI systems like Perplexity and Bing use retrieval-augmented generation (RAG), where the model fetches content in real time. In these cases, proper indexing, clean structure, and crawlability are key.
Hybrid Models: Some models blend both methods. Google SGE, for instance, uses real-time data from the web plus internal knowledge graphs. This means fresh, structured, crawlable content is more likely to be surfaced.
The Future of GEO: What’s Coming Next?
GEO is just beginning, but several developments are on the horizon:
AI-specific Metadata Standards: We may soon see new schema types, microformats, or even AI-specific markup that helps engines interpret content for synthesis.
Author Attribution Protocols: Open standards like MCP (Model Context Protocol) from Anthropic may give sites more control over how their content is cited and attributed in LLM outputs.
Traffic Analytics from AI Engines: Today, GEO's performance is hard to measure. But in the near future, we might get visibility into how often our content is cited in AI answers—just like we track SEO traffic today.
Generative Discovery Platforms: New interfaces (like Perplexity Pages or Arc’s Browse AI) are emerging, where users discover content through AI interfaces rather than traditional search engines. Content optimized for these interfaces will gain first-mover advantage.
A Mental Shift for Creators and Publishers
To succeed in this new landscape, content creators need to reframe their strategy:
Don’t just chase clicks. Focus on being useful.
Don’t just rank on Google. Aim to be cited in answers.
Don’t just think about humans. Write for the machines that write for humans.
In this world, your content is no longer just a destination. It’s an ingredient in someone else’s answer.
That might feel uncomfortable. But it’s also a powerful opportunity to scale your reach, if you optimize for it.
GEO is what SEO was in 2003.
It’s early, it’s evolving, and most of your competitors aren’t thinking about it yet. But the way people discover content is shifting. Fast.
Optimizing for generative engines is no longer optional. If you want to be seen, shared, and cited in the age of AI, you need to write for the machines that write for humans.